Reuben Notes
Skin Layers
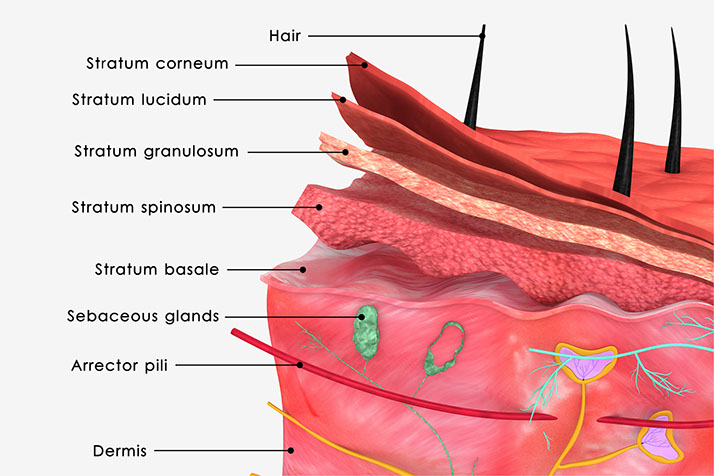
Epidermis
-
Stratum Corneum
- Horny, Keratin Layer
-
Stratum Lucidum
- Seen with thick horny layer (palms & soles)
-
Stratum Granulosum
- Granular Layer
-
Stratum Spinosum
- Prickle, Spiny Layer
- Langerhans Cells: Function as macrophage of the epidermis and process contact antigens
-
Stratum Germinativum
- Basal cell layer
-
-
Basal Cell Keratinocyte:
only cell of the epidermis capable of division.
- They divide and migrate upward.
- Total turnover time is 28 days (14 days of migration and 14 days to be discarded)
-
Melanocyte:
Produces malanin which is transferred to keratinocytes.
- Melanin protects the skin from UV Radiation.
- In whites, found mostly in basal cell layer.
- In blacks, found throughout the epidermis.
-
Basal Cell Keratinocyte:
only cell of the epidermis capable of division.
Dermal-Epideramal Junction (Basement Membrane)
- Lamina Lucida
- Lamina Densa
- Sublamina Densa
Dermis
-
Papillary Dermis:
Immediately beneath epidermis.
- Thin haphazardly arranged collage fibers, abundant ground substance, and delicate elastic fibers
-
Reticular Dermis:
extends to the subcutanous fat.
- Coarse elastic fibers and thick collagen bundles arranged mostly parallel to skin surface
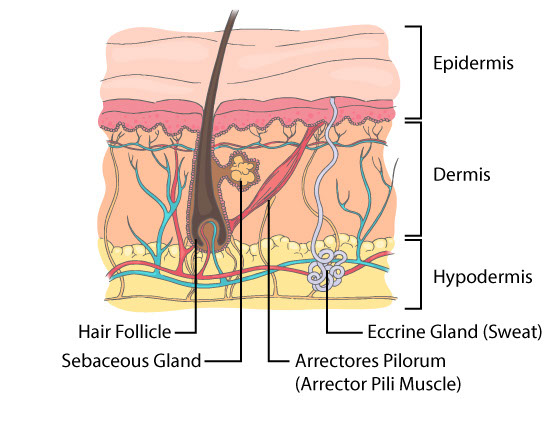
Skin Structures
Hair Follicle
-
Hair growth proceeds through distinct phases
- Anagen: prolonged growth
- Catagen: short lived interphase
- Telogen: final resting phase
- Cells of hair bulb produce hair shaft which is completely keratinized and has no living cells.
- Hair color is due to the amount and type of melanin.
Eccrine Glands
- Found in highest concentration on palms, soles, and axillae.
- Secretory coil located in dermis, transmits sweat directly to skin surface for cooling of body
Apocrine Glands
- Found primarily in axillae and anogenital regions and serves as a scent gland.
- derived from hair germ and opens directly into pilosebaceous follicle rather than skin surface.
- Become active at puberty
Sebaceous Glands
- Found on all body parts except palms and soles
- Produces oil (sebum) that is emptied into the hair follicle.
- Lubricates and protects the hair and skin
Arrectores Pilorum
- Smooth muscle attached to the base of the hair follicle
- Contract in response to cold or fright
- "goose bumps"
 Primary LesionsMacule:Circumscirbed, Flat (without elevation or depression), Nonpalpable change in skin color. <1 cm in diameter.e.g., freckle, petechiae
Primary LesionsMacule:Circumscirbed, Flat (without elevation or depression), Nonpalpable change in skin color. <1 cm in diameter.e.g., freckle, petechiae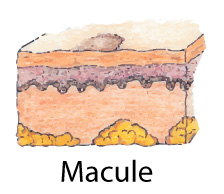 Patch:Similar to macule but > 1 cm Papule:Palpable, circumscribed, solid elevation,Less than 1 cm in diametere.g., elevated nevus
Patch:Similar to macule but > 1 cm Papule:Palpable, circumscribed, solid elevation,Less than 1 cm in diametere.g., elevated nevus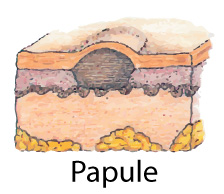 Wheal:Irregularly shapedElevated area or superficial localized edemavaries in sizeEdematous papulee.g., hive, mosquito bite
Wheal:Irregularly shapedElevated area or superficial localized edemavaries in sizeEdematous papulee.g., hive, mosquito bite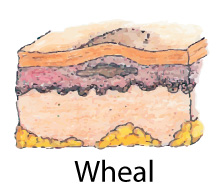 Nodule:Elevated solid massDeeper and firmer than papule1-2 cme.g., wart
Nodule:Elevated solid massDeeper and firmer than papule1-2 cme.g., wart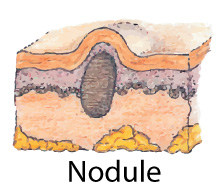 Tumor:Solid mass that extends deep through subcutaneous tissuesimilar to Nodulelarger than 2 cme.g., epithelioma
Tumor:Solid mass that extends deep through subcutaneous tissuesimilar to Nodulelarger than 2 cme.g., epithelioma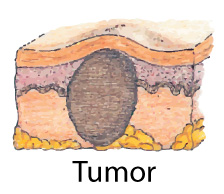 Plaque:an elevation above the skin with a plateau-like surface. Vesicle:Circumscribed elevation of skinfilled with serous fluidless than 1cm.e.g., herpes simplex, chickenpox
Plaque:an elevation above the skin with a plateau-like surface. Vesicle:Circumscribed elevation of skinfilled with serous fluidless than 1cm.e.g., herpes simplex, chickenpox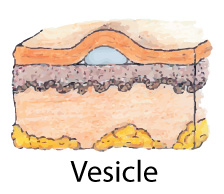 Bulla:Similar to vesicle but > 1 cm. Pustule:Circumscribed elevation of skinSimilar to vesicle but filled with neutrophils and dead bacteria.Fluid is white or yellow (pus)Varies in sizee.g., acne, staphylococcal infection
Bulla:Similar to vesicle but > 1 cm. Pustule:Circumscribed elevation of skinSimilar to vesicle but filled with neutrophils and dead bacteria.Fluid is white or yellow (pus)Varies in sizee.g., acne, staphylococcal infection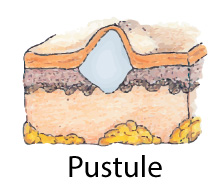 Secondary LesionsScale:an excess of horny material on the skinCrust:scab consisting of dried blood, serum, or pusErosion:Scooped out and shallow break. No damage to the dermisFissure:linear form of an erosionUlcer:Deep lesion involving the dermisEschar:Dark colored, hard to remove crust on ulcer Shapes and Arrangements of LesionsAnnular:round lesion, ring-like.The rim is different from the centerLinear:long, thin lesion or smaller lesions in a long, thin line.Target or Iris:Concentric rings like an arches target.Imbricated:Target lesions with near form of an erosionSerpiginous:Snake-like.Partially circular and undulatingGeographic:Outline of a continent on a mapVegetating:Lesion has a surface that grows outward in uneven, fleshy tufts that feel soft.Verrucous:Wart-LikeTufts of protruding lesion are hyperkeratotic, not soft.Zosteriform:Conforming to the distribution of a nerve root.Polycyclic or Circinate:Annular lesions grow together, Parts of their cirlces form larger lesion.Grouped:Several similar lesions located in close proximity surrounded by a large area of normal skin Morphology of LesionsThe following aspects should be included in every description:SizeColorConsistency: Soft, Medium, FirmConfiguration: Shape or outline of lesionMargination: sharp or diffuseSurface Characteristics: Smooth or rough
Secondary LesionsScale:an excess of horny material on the skinCrust:scab consisting of dried blood, serum, or pusErosion:Scooped out and shallow break. No damage to the dermisFissure:linear form of an erosionUlcer:Deep lesion involving the dermisEschar:Dark colored, hard to remove crust on ulcer Shapes and Arrangements of LesionsAnnular:round lesion, ring-like.The rim is different from the centerLinear:long, thin lesion or smaller lesions in a long, thin line.Target or Iris:Concentric rings like an arches target.Imbricated:Target lesions with near form of an erosionSerpiginous:Snake-like.Partially circular and undulatingGeographic:Outline of a continent on a mapVegetating:Lesion has a surface that grows outward in uneven, fleshy tufts that feel soft.Verrucous:Wart-LikeTufts of protruding lesion are hyperkeratotic, not soft.Zosteriform:Conforming to the distribution of a nerve root.Polycyclic or Circinate:Annular lesions grow together, Parts of their cirlces form larger lesion.Grouped:Several similar lesions located in close proximity surrounded by a large area of normal skin Morphology of LesionsThe following aspects should be included in every description:SizeColorConsistency: Soft, Medium, FirmConfiguration: Shape or outline of lesionMargination: sharp or diffuseSurface Characteristics: Smooth or rough